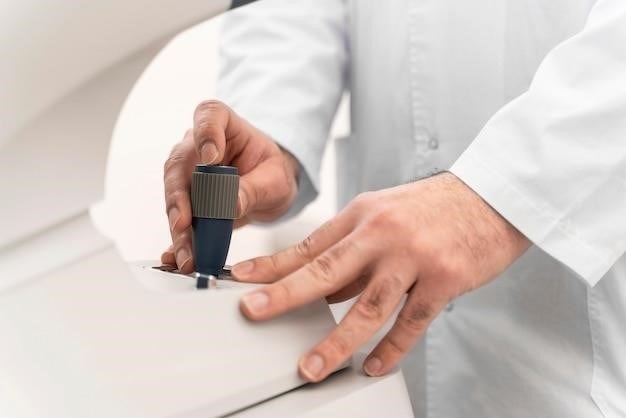
Manual Keratometer⁚ An Overview
Manual keratometers‚ also known as ophthalmometers‚ measure corneal curvature. Developed by von Helmholtz‚ they use mires or prisms reflecting off the cornea to determine astigmatism and corneal power. These devices provide crucial data for eye care professionals.
Types of Manual Keratometers
While the fundamental operating principle remains consistent across manual keratometers‚ variations exist in design and features; Historically significant instruments include the Helmholtz keratometer‚ a foundational design that established the core principles of corneal curvature measurement. Bausch & Lomb and Javal-Schiotz keratometers represent further developments‚ each offering refinements in precision‚ ease of use‚ or specific measurement capabilities. These variations often involved adjustments to the mire system‚ the illumination source‚ or the overall ergonomics of the device. Modern manual keratometers may incorporate updated optical components or improved magnification systems to enhance accuracy and user comfort‚ while still retaining the manual adjustment aspect central to their operation. The specific model used can influence the precision and ease of obtaining reliable measurements.
Operating Principles of Manual Keratometers
Manual keratometers operate on the principle of reflection‚ utilizing the cornea’s convex surface as a mirror. A precisely calibrated mire system‚ often consisting of illuminated targets or patterns‚ is projected onto the cornea. The examiner then manually adjusts the mires until a clear‚ superimposed image is observed. The degree of adjustment needed to achieve this alignment directly correlates to the corneal curvature. This process measures the power of the cornea in different meridians‚ revealing the presence and amount of astigmatism. The reflected image’s characteristics – its size‚ shape‚ and position relative to the mires – are meticulously analyzed to determine the corneal curvature in diopters. The instrument’s design incorporates optical components to magnify the reflected image‚ facilitating precise measurements. The accuracy depends on the operator’s skill in aligning the mires and interpreting the resulting image.
Using a Manual Keratometer
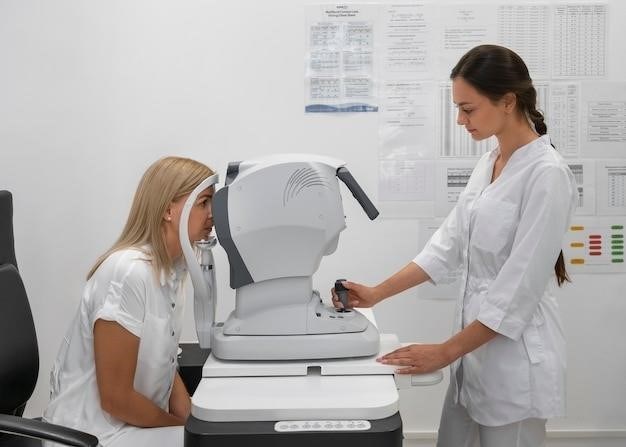
Employing a manual keratometer involves precise patient positioning and instrument setup‚ followed by careful measurement and subsequent result interpretation. Accurate technique is crucial for reliable readings.
Patient Positioning and Instrument Setup
Proper patient positioning is paramount for accurate measurements with a manual keratometer. The patient should be seated comfortably‚ ensuring their chin rests snugly in the chin rest and their forehead is firmly against the headrest. This stable position minimizes head movement during the procedure. The instrument should then be carefully adjusted to point directly at the eye being examined. A clear‚ bright ring in the center of the cornea (the corneal image of the circular mire) indicates correct positioning. From the side‚ the practitioner should verify the patient sees a red fixation light within the instrument’s tube. These steps ensure the instrument is aligned precisely with the cornea for optimal readings. Before proceeding‚ double-check the patient’s comfort level and instrument stability to avoid errors. Any adjustments to seating or instrument position should be made with care to maintain the established alignment. Accurate positioning eliminates parallax and ensures the instrument’s optical axis is aligned with the corneal surface. This is critical for obtaining repeatable and reliable measurements of corneal curvature. Failure to follow these guidelines may result in inaccurate readings and potentially compromise the assessment of corneal astigmatism.
Performing the Measurement
Once the patient is properly positioned and the instrument is correctly aligned‚ the measurement process begins. The examiner uses the focusing knob to bring the mires or prisms into sharp focus on the cornea. This involves adjusting the instrument until a clear‚ doubled image of the mires is observed. Precise manipulation of the focusing mechanism is crucial for accurate results. The examiner then rotates the instrument’s measuring drums to align the mires with the corneal reflections. This alignment process requires careful observation and precise adjustments. The positions of the mires are then read from the calibrated scales on the drums. These readings directly correspond to the corneal curvature in the two principal meridians. Readings should be taken for both the horizontal and vertical meridians. The difference between the readings provides a measure of corneal astigmatism; Throughout the measurement process‚ the examiner must maintain a stable position and avoid any sudden movements to ensure the accuracy of the readings. Recording the readings is essential. Precise notation of the measurements is crucial to prevent errors in interpretation. Multiple measurements may be taken to ensure reliability‚ and any significant discrepancies should be investigated. Careful and methodical execution of the measurement process is essential for obtaining accurate and reliable corneal curvature data.
Interpreting the Results
The readings obtained from a manual keratometer provide crucial information about the corneal curvature. The readings represent the refractive power of the cornea in diopters (D) for the two principal meridians—typically horizontal and vertical. The difference between these two readings indicates the amount of corneal astigmatism present. A larger difference signifies a higher degree of astigmatism. The axis of astigmatism‚ representing the orientation of the corneal irregularity‚ is also determined. This is usually expressed in degrees‚ indicating the direction of the most curved meridian. Understanding the axis is crucial for fitting corrective lenses or designing surgical procedures. The examiner must carefully record these values‚ including both the power and axis‚ for each meridian. Accurate recording prevents misinterpretations and ensures that the data can be used effectively for diagnosis and treatment planning. Further analysis may involve comparing the keratometry readings to other clinical findings‚ such as refractive error measurements and patient symptoms. These comparisons help establish a complete clinical picture. The interpretation of results should always be done in the context of the overall clinical picture and the patient’s individual history. Improper interpretation can lead to inaccurate diagnoses and ineffective treatment strategies. Experienced clinicians are best equipped to interpret keratometry results to ensure accurate diagnosis and treatment.
Maintenance and Calibration
Regular cleaning and disinfection of the instrument’s optical components and surfaces are essential. Calibration should be performed periodically by qualified personnel to ensure accuracy and reliable measurements. Proper handling prevents damage.
Cleaning and Disinfection
Cleaning and disinfecting a manual keratometer is crucial for maintaining its accuracy and preventing the spread of infection. Before commencing any cleaning procedure‚ always refer to the manufacturer’s instructions specific to your keratometer model. These instructions will provide detailed guidance on appropriate cleaning solutions and techniques. Generally‚ the process involves several steps. First‚ switch off the instrument and disconnect it from the power supply. Then‚ gently remove any loose debris from the instrument’s surfaces using a soft‚ lint-free cloth or brush. Avoid using abrasive materials that could scratch the delicate optical components. Next‚ carefully clean the optical surfaces (mirrors‚ lenses‚ etc.) with a specialized lens cleaning solution and a clean‚ soft lens tissue. Avoid excessive pressure‚ and use gentle strokes to prevent damage. After cleaning‚ allow the instrument to air dry completely before use. For disinfection‚ use a suitable disinfectant solution recommended by the manufacturer. Apply the solution according to the manufacturer’s instructions‚ ensuring complete coverage of all surfaces. Allow the disinfectant to dwell for the recommended contact time before wiping it off with a clean‚ lint-free cloth. Always ensure the instrument is completely dry before using it on a patient. Regular cleaning and disinfection protocols are essential for maintaining the hygiene and accuracy of the manual keratometer.
Troubleshooting Common Issues
Troubleshooting a manual keratometer often involves addressing issues related to image clarity‚ measurement inconsistencies‚ and operational malfunctions. Blurred images frequently stem from improper focusing or dirty optical surfaces. Always begin by carefully cleaning all lenses and mirrors using a lens cleaning solution and a soft cloth‚ as described in the manufacturer’s instructions. If the problem persists‚ check the instrument’s alignment and adjust accordingly. Inconsistent measurements may indicate a problem with the instrument’s calibration. Regular calibration checks are essential for maintaining accuracy. Refer to the manufacturer’s instructions for calibration procedures‚ and consider professional recalibration if needed. If the instrument’s light source malfunctions‚ check the power supply and the lamp itself. Replace the lamp if necessary‚ following the manufacturer’s guidance. Mechanical issues‚ such as stiff moving parts‚ may require lubrication. However‚ before attempting any maintenance‚ consult the manufacturer’s instructions. If you’re unable to resolve the issue after attempting these basic troubleshooting steps‚ it is advisable to contact a qualified service technician for professional assistance. Attempting complex repairs without proper training could damage the equipment further. Always prioritize the safety and accuracy of the instrument.

Safety Precautions
Always follow manufacturer instructions. Handle the instrument with care to avoid damage. Ensure proper patient positioning for safety and accurate readings. Regular cleaning and disinfection are crucial.
Important Safety Instructions
Before operating a manual keratometer‚ carefully read and understand the manufacturer’s instructions. Always ensure the instrument is properly calibrated and maintained to guarantee accurate measurements and prevent errors that could lead to misdiagnosis or inappropriate treatment. Never attempt to repair or adjust internal components yourself; instead‚ contact a qualified technician for service. Handle the instrument with care to avoid damage to the delicate optical components. Protect the device from dust‚ moisture‚ and extreme temperatures‚ storing it in a clean‚ dry environment when not in use. Maintain hygiene by cleaning and disinfecting the instrument before and after each use following the manufacturer’s recommended procedures. Use appropriate cleaning solutions and avoid abrasive materials that could scratch the surfaces. If liquid spills onto the instrument‚ immediately disconnect it from the power source and allow it to dry completely before resuming operation. Always prioritize patient safety by ensuring proper positioning and maintaining a calm and reassuring environment to minimize discomfort and maximize cooperation; Regular inspection of all parts is crucial to identify any potential issues. Always consult a qualified professional for any uncertainties. Adhering to these guidelines ensures safe and reliable operation of the manual keratometer.
Emergency Procedures
In the unlikely event of malfunction‚ immediately cease operation and disconnect the keratometer from any power source. If a patient experiences discomfort or adverse reaction during measurement‚ immediately stop the procedure and provide necessary first aid or medical attention as appropriate. If any liquid spills onto the instrument‚ immediately disconnect it and allow it to dry thoroughly before attempting to use it again. Do not attempt any repairs yourself; contact qualified service personnel immediately for any issues. Should the instrument sustain significant damage‚ discontinue its use and notify the manufacturer or distributor immediately. Report any incidents or accidents‚ no matter how minor‚ to the appropriate authorities and document the event thoroughly. Familiarize yourself with your institution’s emergency protocols and procedures and ensure that you can access and use any necessary emergency equipment. Keep emergency contact information readily available‚ including the manufacturer’s contact details and relevant medical personnel. Following these steps will help ensure prompt and effective response to any unforeseen circumstances. Regular training and refresher courses on emergency procedures are strongly recommended.
